In the context of insufficient world economic growth, China's "One Belt and One Road" initiative is a major strategy to promote economic cooperation and development. The proposal and its gradual implementation have injected new vitality into the process of accelerating economic globalization and China's economic growth. The new type of economy represented by Internet enterprises is also actively diffusing across borders. Cross-border e-commerce is experiencing explosive growth and has become a new driving force for trade development. Therefore, cross-border e-commerce can be expected to play vital role in the construction of international trade in the context of the "One Belt and One Road" strategy.
The link between commodity flows and capital flows involve many links, which affect the efficiency and cost of overall trade activity. Customs clearance efficiency problems, tax rebate settlement problems, and small and medium enterprise financing difficulties are all trade cost and efficiency problems that are yet to be solved. This report by Runbo Research Center for Digital Finance, THUIFR, examines these issues to get insights to address these problems.
Overview of China’s cross-border e-commerce development and its significance
Cross-border e-commerce refers to transaction activity that crosses different customs borders. It is an international business activity which involves transactions through e-commerce platforms, electronic payment and settlement mechanisms, and goods delivery through cross-border e-commerce logistics including long-distance storage to complete the transaction.
Overview of the development of domestic cross-border e-commerce
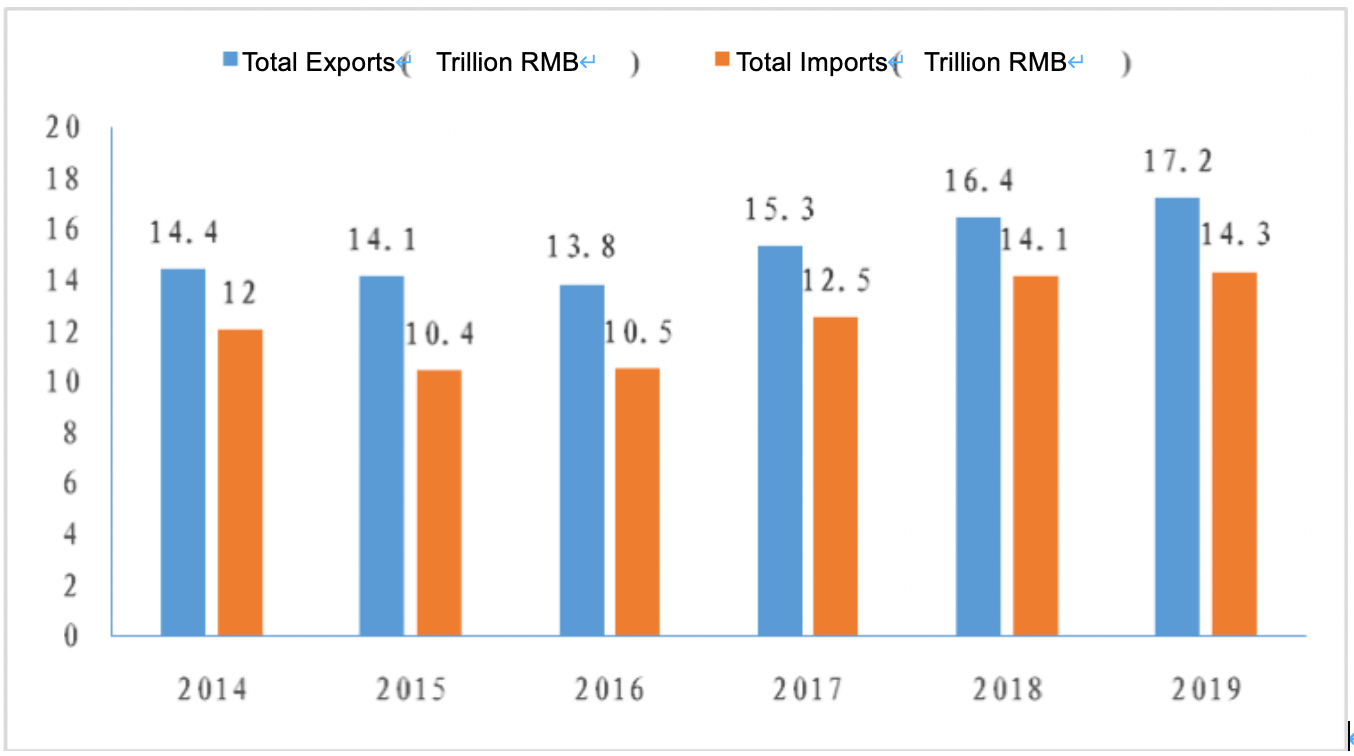
Because of the explosive growth of the mobile Internet, cross-border e-commerce platforms linkages are shorter than traditional trade circulation linkages, are more timely and` enabling link data sharing and direct access to consumer terminals. Cross-border e-ecommerce has become a new way for Chinese manufacturing to link with global consumers and has gradually become a new driving force for the development of international trade. China's cross-border e-commerce exports exceeded 1.9 trillion RMB in 2019 (see figure 1). In the past six years, the proportion of China's cross-border e-commerce exports in its foreign trade has increased from 2.2% to 11.25%. More and more cross-border e-commerce exporters have entered major cross-border e-commerce platforms around the world. Taking Amazon as an example, among the new global sellers on Amazon in 2019, Chinese sellers still have an absolute advantage.
The importance of developing China’s cross-border e-commerce
Economic significance: as a product of globalization, cross-border e-commerce is an important carrier for allocating resources in the world market. It can further break down barriers in the global market and promote cross-border commercial circulation and it will expand the international reach of Chinese enterprises and contribute to the country's export earnings.
Social significance: the participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in international trade not only regulates their operating behaviors, cross-border e-commerce also creates a more virtual digital sales network. This greatly reduces the transaction costs between producers and global consumers, enabling enterprises to trade directly with global suppliers and customers. For small and medium-sized enterprises, e-commerce reduces the "distance" to joining large global markets. As more companies enjoy the global dividend, globalization helps to promote a more equal and inclusive global trade system. Further, the flat online distribution model of cross-border e-commerce imports reduces many intermediate links, resulting in a drop in the price of overseas products. By bringing the world's high-quality consumer goods into the domestic market, China will cultivate the domestic market with overseas products and lead the industry to speed up the transformation and consumption upgrading, ultimately benefiting domestic consumers.
Brand significance: Internet platforms enables foreign consumers to get access to domestic high-quality, inexpensive and practical goods, which helps Chinese national brands to go global, to start their own global brands and to build the reputation of China’s global brand. Under the influence of global consumers, internet platforms enable Chinese enterprises to continuously improve the quality of their products and make the leap from "made in China" to "quality in China".
Bottlenecks restricting the development of cross-border e-commerce in China
Customs clearance under customs supervision
Domestic commodity exporting SMEs still use the small postal package service under the UPU system, even though it is higher cost and less timely than new digital solutions. For example, the "9610" export supervision method is not fully popularized in the comprehensive test zone of cross-border e-commerce. Due to the methods high requirements for digital solutions, it is necessary to connect with the commodity, logistics, inspection and other systems, and to connect with the customs, settlement and other administrative systems, check-up system, docking the customs administrative system, settlement, etc.
The comprehensive service capacity of cross-border e-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce export commodities and capital circulation involve multiple links, and the whole service chain is long and complex, which affects the circulation efficiency and cost of the entire value chain:
The flow of goods includes nine steps to reach the Customer terminal. During this process, there are uncontrollable factors affecting efficiency and cost of China’s domestic customs inspection, including the reliability of overseas warehouses and the timeliness of overseas logistics.
Capital flow also need to flow through nine nodes before it can return to e-commerce producers: consumer, payment, platform, transfer, third-party account, foreign exchange settlement and settlement, cross-border e-commerce export enterprise, payment, supplier or service provider.
The difficulty and high cost of financing for cross-border export enterprises
In the process of seeking development and improving competitiveness, cross-border export enterprises have the need to use capital and constantly looking for profitable spaces to operate in. In terms of foreign exchange business, export trade financing and other fields are faced with many problems, such as asymmetric information and complex audit process under Banks auditing authenticity reviews. For this reason, trade financing business often requires enterprises to provide more collateral, guarantee and other relevant safeguard measures, which increases the financing cost and difficulty of enterprises. The business scale of the banking sector is shrinking, which affects the profitability of export enterprises.
Implications for promoting the development of cross-border e-commerce in the future
Investigation and research reveals that the development bottleneck faced by cross-border e-commerce is not due to the lack of policy guarantee, but to the need to solve problems around trade process implementation. Blockchain, big data, artificial intelligence and other technologies can be used to develop comprehensive cross-border e-commerce service platforms to solve the four outstanding problems identified above. Such a platform infrastructure could provide solutions for the process management of goods and funds of export enterprises, including sales, customs clearance, logistics, tax refunds, foreign exchange, after-sales service, supply chain finance and so on. Such as platform could integrate foreign trade resources such as banking, insurance, commodity inspection, and provides one-stop foreign trade services for enterprises by combining overseas warehouses and overseas marketing networks.


